Improving the reliability of Wi-Fi Hotspots
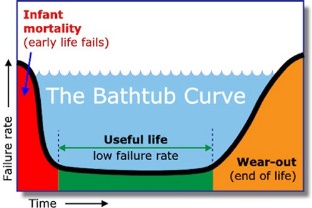
Any machine will fail sooner or later. Failure usually follows the ‘bathtub curve’. When new equipment is installed then there is an initial high failure rate followed by a long period of time with a low failure rate. Finally failures increase as equipment ‘wears out’.
When a business provides a Wi-Fi Hotspot service for a group of people and the service fails then the business will receive many complaints. The business can purchase high reliability but cannot get a guarantee of 100% reliability from the phone or cable company that provides the connection to the Internet.
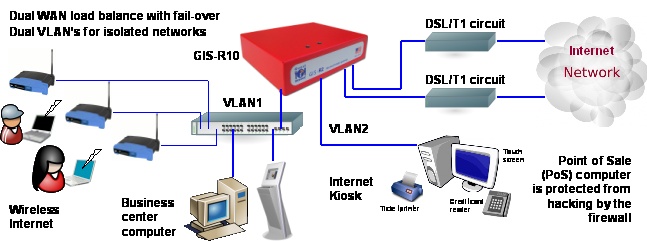
A practical solution to the problem of improving the reliability of the Internet connection is to lease two Internet connections from two different providers. The phone company can be contracted to provide a DSL or a T1, and the cable company can be contracted to provide a broadband modem. The two Internet services are connected to a hotspot gateway that has the features to work with two service providers.
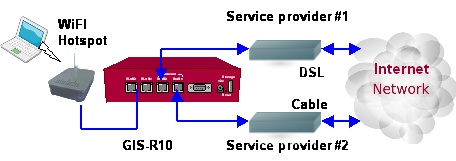
The Hotspot gateway shown in the diagram has two Internet or WAN (wide area network) connectors. Each WAN connector links to an Internet service from one provider. Two WAN connectors mean that Internet service is obtained via two providers.
The Dual-WAN Hotspot gateway as a feature called ‘fail-over’, this means that when the Internet service from one of the providers fails then the Hotspot customers still get Internet access from the other provider.
The dual-WAN hotspot gateway can also improve the speed of Internet access by routing the Hotspot customer traffic over both WAN connections. The aggregate Internet speed is the sum of the two Internet WAN connections. E.g.
- Provider 1 Internet speed = 6Mb/s
- Provider 2 Internet speed = 3 Mb/s
- Total aggregate Internet speed = 9Mb/s
The dial-WAN Wi-Fi Hotspot network for a hotel might look like the diagram below.