A business that provides an Internet connection for paying customers is called an ISP (Internet service provider) or a WISP (Wireless Internet service provider). A business can become an ISP by leasing a high bandwidth Internet connection (DSL, cable or T1) and then reselling the Internet access to a number of customers.
An ISP or Hotspot operator can usually make money in locations where travelers have a break during a journey. Airports, marinas, RV parks and train stations are all places where money can be made by selling Internet access.
The internet Hotspot service can be provided in two different formats. The first is a WiFi Hotspot for users who carry laptops, netbooks, iPads® or WiFi equipped phones. The second is a kiosk for users who need to check emails but don’t have a computer.
A WiFi Hotspot gateway can connect both wireless kiosk customers. Wireless access points and kiosks are connected to the gateway. The charge for service is identical for both types of services. Customers can type in their credit card information to purchase access to the Internet. If a point of sale (e.g. gift shop, etc) is close to the Internet service then scratch cards can be sold to customers.
An Internet kiosk can be a desk top computer that is connected to the Hotspot gateway. Kiosks are also custom manufactured with robust keyboards and screens, and have graphics that advertise the service.
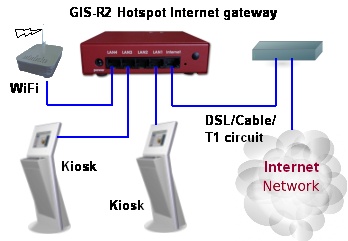
The kiosk computers and wireless access point are connected to a Hotspot gateway that provides the login screen and has all the features for customer billing. Credit card billing is routed to a specialized service such as that provided by PayPal®. The equipment is connected as shown in the diagram below.